
Layer 3 switch uses ASICs for forwarding decisions. Hardware/Software decision making – The key difference between Layer 3 switch and router lies in the hardware technology used to making forwarding decision.Router is the front runner in such scenario where WAN technologies such as Frame Relay or ATM need to be fostered. However, when it comes to working on WAN and edge technologies, Layer 3 switch lags behind. WAN technologies support – Layer 3 switch is limited to usage over LAN environment where Inter VLAN routing can be performed.It means that you can configure a Layer 3 switch to operate as a normal Layer 2 switch. Flexibility – Layer 3 switch allows you to mix and match Layer 2 and Layer 3 switching.Port density – Layer 3 switch has much higher port count while router has a lower port density than Layer 3 switch.High performance router is typically much more expensive than Layer 3 switch. Cost – Layer 3 switch is much more cost effective than router for delivering high-speed inter-VLAN routing.On this account, Layer 3 switches separates ports into VLANs and perform the routing between them, in addition to supporting routing protocols such as RIP, OSPF and EIGRP. It can switch packets by checking both IP addresses and MAC addresses.
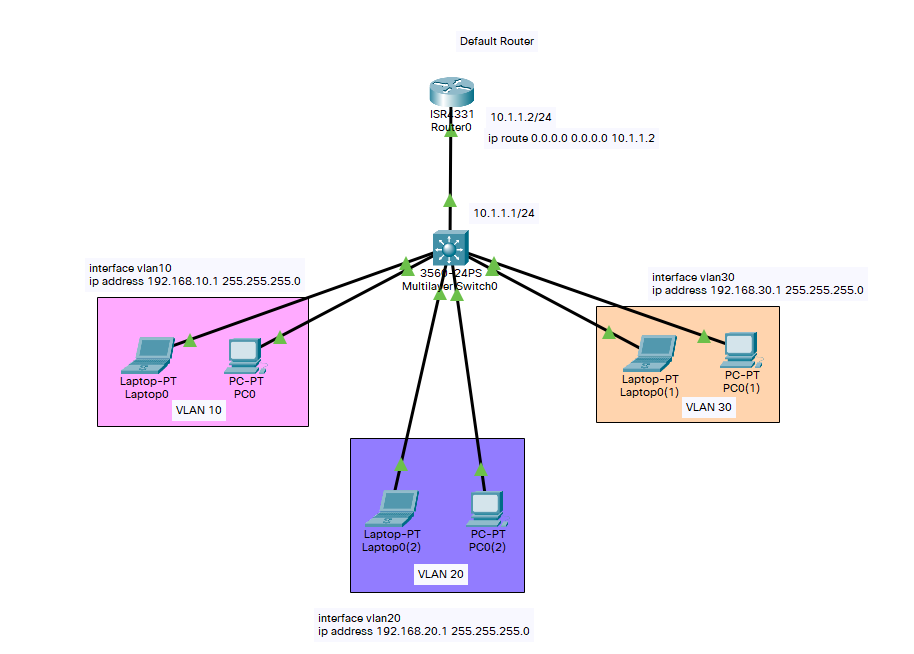
So Layer 3 switch is a switch that can route traffic, and a router with multiple Ethernet ports has a switching functionality.
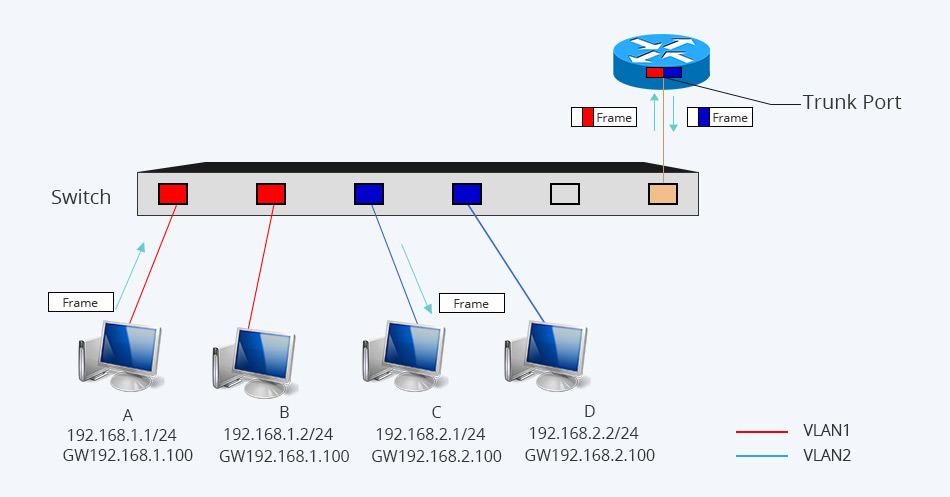
A Layer 3 switch is both a switch and a router. It is a specialized hardware device used in network routing, which is conceived as a technology to improve network routing performance on large local area networks (LANs) like corporate intranets. Layer 3 switch is also called multilayer switch. So what is on earth Layer 3 switch and how is it different from router? For this reason, many networking beginners are puzzled over the definition and purpose of a Layer 3 switch. Layer 3 switches have a lot in common with traditional routers: they can also support the same routing protocols, inspect incoming packets and make dynamic routing decisions based on the source and destination addresses inside.
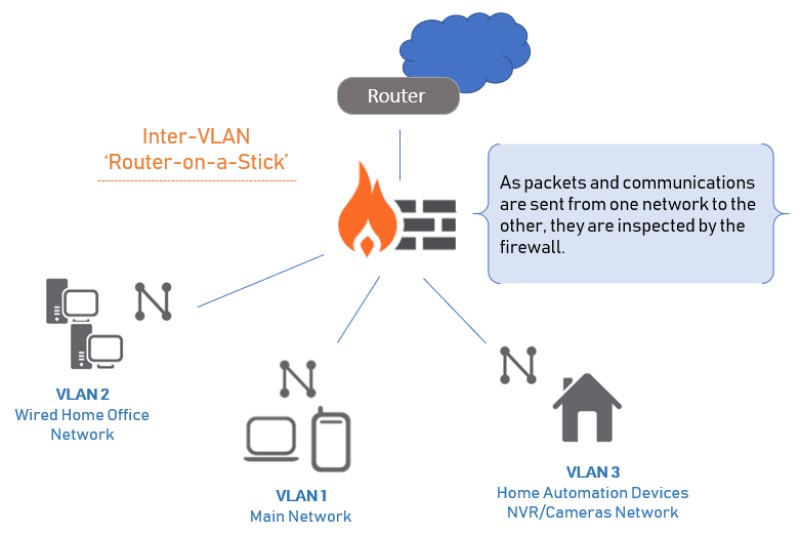
Besides, switches are understood to be forward traffic based on MAC address, while routers perform the forwarding based on IP address. In the OSI model, we know that traditional network switches operate at Layer 2 while network routers operate at Layer 3.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
